`Busting the 8 biggest Windows myths

Windows is the most popular operating system in the world, but it also has a lot of myths and misconceptions surrounding it. In this blog post, we will debunk some of the most common ones and explain why they are not true. Let’s get started!

Myth 1: USB sticks must be ejected!
You have probably seen the message «Safely remove hardware and eject media» when you plug in a USB stick or an external hard drive to your Windows PC. This message suggests that you need to click on it and wait for a confirmation before you can unplug your device. But is this really necessary?
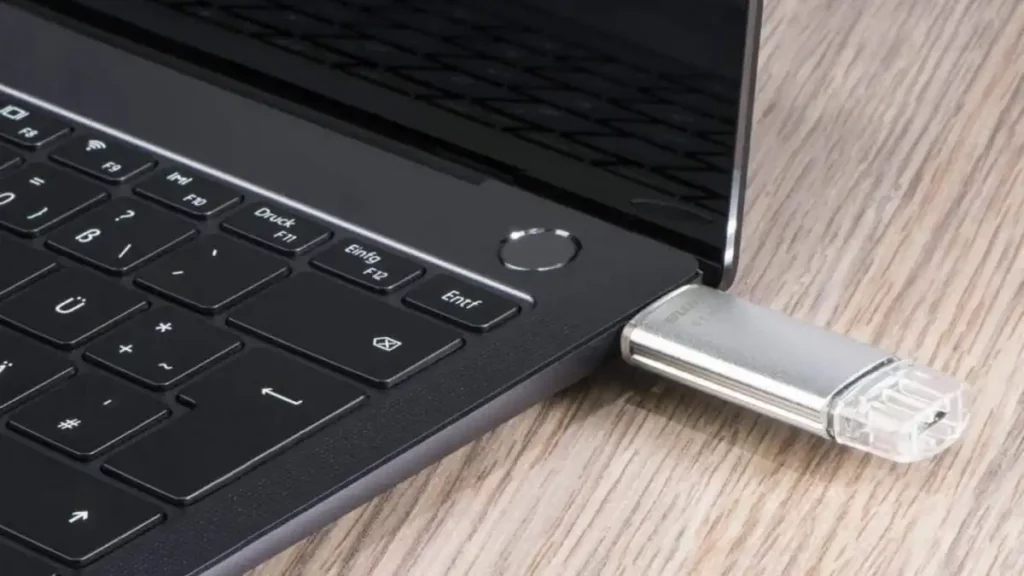

The answer is: not always. Windows has a feature called «write caching» that allows it to improve the performance of your device by temporarily storing data in memory before writing it to the disk. This means that sometimes, when you unplug your device, there might be some data that has not been written yet, and you could lose it or corrupt your files.
However, Windows also has another feature called «quick removal» that disables write caching for removable devices. This means that Windows writes data to your device as soon as possible, and you can safely unplug it without waiting for a confirmation. By default, Windows enables quick removal for most removable devices, so you don’t have to worry about ejecting them.
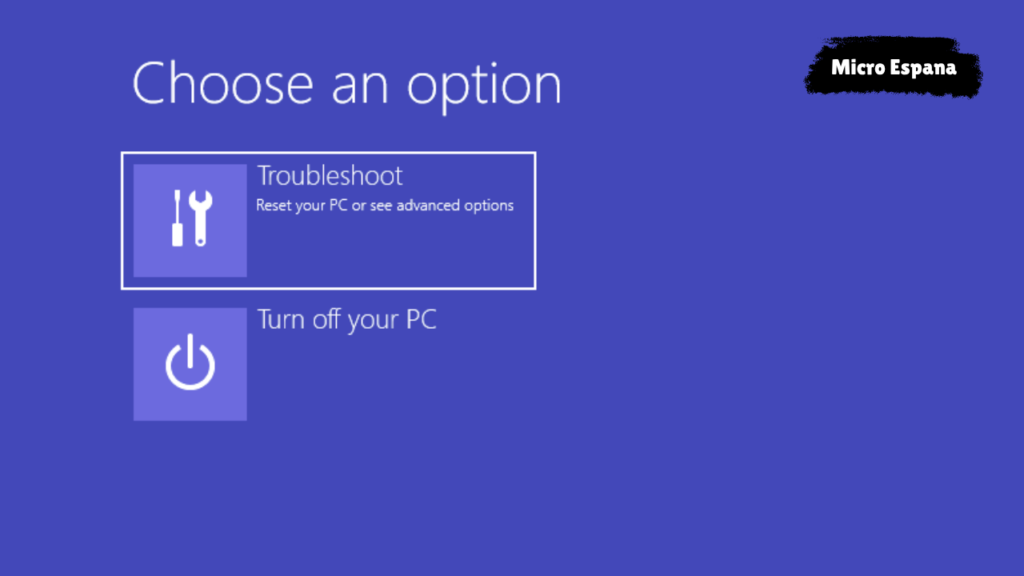
To check if your device has quick removal enabled, you can follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Disk Management.
- Find your device in the list of disks and right-click on it.
- Select Properties and then click on the Policies tab.
- If you see «Quick removal» selected, then you can safely unplug your device without ejecting it.
- If you see «Better performance» selected, then you should eject your device before unplugging it.
Myth 2: Drives must be defragmented regularly!
You have probably heard that defragmenting your drives can improve their performance and speed up your Windows PC. But what does defragmenting mean and why is it necessary?
Defragmenting is the process of reorganizing the data on your drive so that it is stored in contiguous blocks. This reduces the amount of time that your drive needs to access and read data, and makes it more efficient.
However, defragmenting is not always needed or beneficial. In fact, there are some cases where defragmenting can be harmful or useless:
- If you have a solid state drive (SSD), then you should never defragment it. SSDs do not have moving parts like hard disk drives (HDDs), and they do not suffer from fragmentation. Defragmenting an SSD can actually reduce its lifespan by causing unnecessary wear and tear.
- If you have a modern version of Windows (Windows 10, 8.1, or 8), then you don’t have to worry about defragmenting your drives manually. Windows automatically defragments your drives in the background when your PC is idle, and optimizes them for performance. You can check the status of your drives by going to Settings > System > Storage > Optimize Drives.
- If you have a lot of free space on your drive, then defragmenting it will not make much difference. Fragmentation only affects the performance of your drive when it is nearly full and has to store data in scattered locations.
Myth 3: Antivirus software slows down your PC!
You have probably been told that antivirus software is essential for protecting your Windows PC from malware, viruses, and other threats. But you might also have heard that antivirus software can slow down your PC by consuming a lot of resources and interfering with other programs.
The truth is: it depends on the antivirus software you use. Some antivirus programs are more lightweight and efficient than others, and some offer more features and protection than others. The best antivirus software should balance security and performance, and not compromise one for the other.
One way to measure the impact of antivirus software on your PC is to use benchmarks. Benchmarks are tests that measure various aspects of your PC’s performance, such as speed, memory usage, disk usage, battery life, etc. You can run benchmarks before and after installing an antivirus program to see how much difference it makes.
Another way to evaluate antivirus software is to use reviews and ratings from reputable sources. You can find reviews and ratings from experts and users online, or from magazines and websites that specialize in testing antivirus software. You can compare different antivirus programs based on their features, protection level, ease of use, customer support, price, etc.
Some of the most popular and trusted antivirus software for Windows are:
- Bitdefender
- Kaspersky
- Norton
- McAfee
- Avast
- AVG
Myth 4: Windows Game Mode does not help at all!
You have probably noticed a feature called Game Mode in your Windows settings. Game Mode is a feature that was introduced in Windows 10 to improve the gaming performance of your PC. But does it really work and how does it work?
Game Mode works by optimizing your PC’s resources for gaming. It does this by:
- Giving priority to your game over other processes and programs running in the background.
- Preventing Windows updates and notifications from interrupting your game.
- Adjusting your graphics settings to reduce the load on your GPU.
- Allocating more CPU cores to your game.
However, Game Mode does not guarantee a better gaming experience for every game or every PC. Some games might not benefit from Game Mode at all, or might even perform worse with it. Some PCs might not have enough resources to spare for Game Mode to make a difference. Some users might prefer to customize their own settings and preferences for gaming.
The best way to find out if Game Mode helps your game or not is to try it yourself. You can enable or disable Game Mode by following these steps:
- Press the Windows logo key + G to open the Game Bar.
- Click on the Settings icon on the Game Bar.
- Click on Gaming and then on Game Mode.
- Toggle the switch to On or Off.
You can also enable or disable Game Mode for specific games by going to Settings > Gaming > Game Mode and clicking on the link «Choose which games can use Game Mode».
Myth 5: Google Chrome consumes a lot of RAM and slows down Windows!
You have probably used Google Chrome as your web browser at some point. Google Chrome is one of the most popular and powerful web browsers in the world, but it also has a reputation for being a resource hog. Many users complain that Google Chrome consumes a lot of RAM and slows down their Windows PC.

But is this true and why does it happen?
The reason why Google Chrome uses a lot of RAM is because of its design. Google Chrome is based on a multi-process architecture, which means that each tab, extension, plugin, and website runs in its own separate process. This makes Google Chrome more stable, secure, and responsive, as it prevents one process from crashing or affecting another.
However, this also means that each process consumes some amount of RAM, and the more processes you have, the more RAM you use. This can be a problem if you have a lot of tabs, extensions, plugins, and websites open at the same time, or if you have a limited amount of RAM on your PC.
Fortunately, there are some ways to reduce the RAM usage of Google Chrome and improve its performance. Here are some tips:
- Close tabs that you are not using or use an extension like OneTab to save them for later.
- Disable or remove extensions that you don’t need or use an extension like Extensity to manage them.
- Update Google Chrome to the latest version as it might have bug fixes and improvements.
- Clear your browsing data regularly by going to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
- Use Task Manager to identify and end processes that are using too much RAM by pressing Shift + Esc while in Google Chrome.